Our pleasure and well-being are inextricably linked to our physical health. It also contributes significantly to our economic advancement, since healthy people live longer and are more productive. Our most frequent health issue is most likely connected to our weight. Over the previous century, several natural and artificial weight-loss strategies have been developed, yet we still don't have enough of them. The majority of us have tried one or both, and some of us don't care. We should, though. We also need to make sure that our priorities are in order. Who doesn't want to be healthy, right?
Low-carb diets have lately acquired popularity among the general public. Low-carb diets have become a dietary habit for millions of individuals throughout the world in the last decade. Low-carb diets are becoming more popular, and for good reason. The ketogenic diet, which is one of the most severe forms of the low-carb diet, has lately attracted a lot of attention. People often inquire about the differences between the two diets: low carb and keto. The low-carb diets, keto diets, and the final battle: Low Carb versus Keto Diet will be discussed in the following parts of the article.
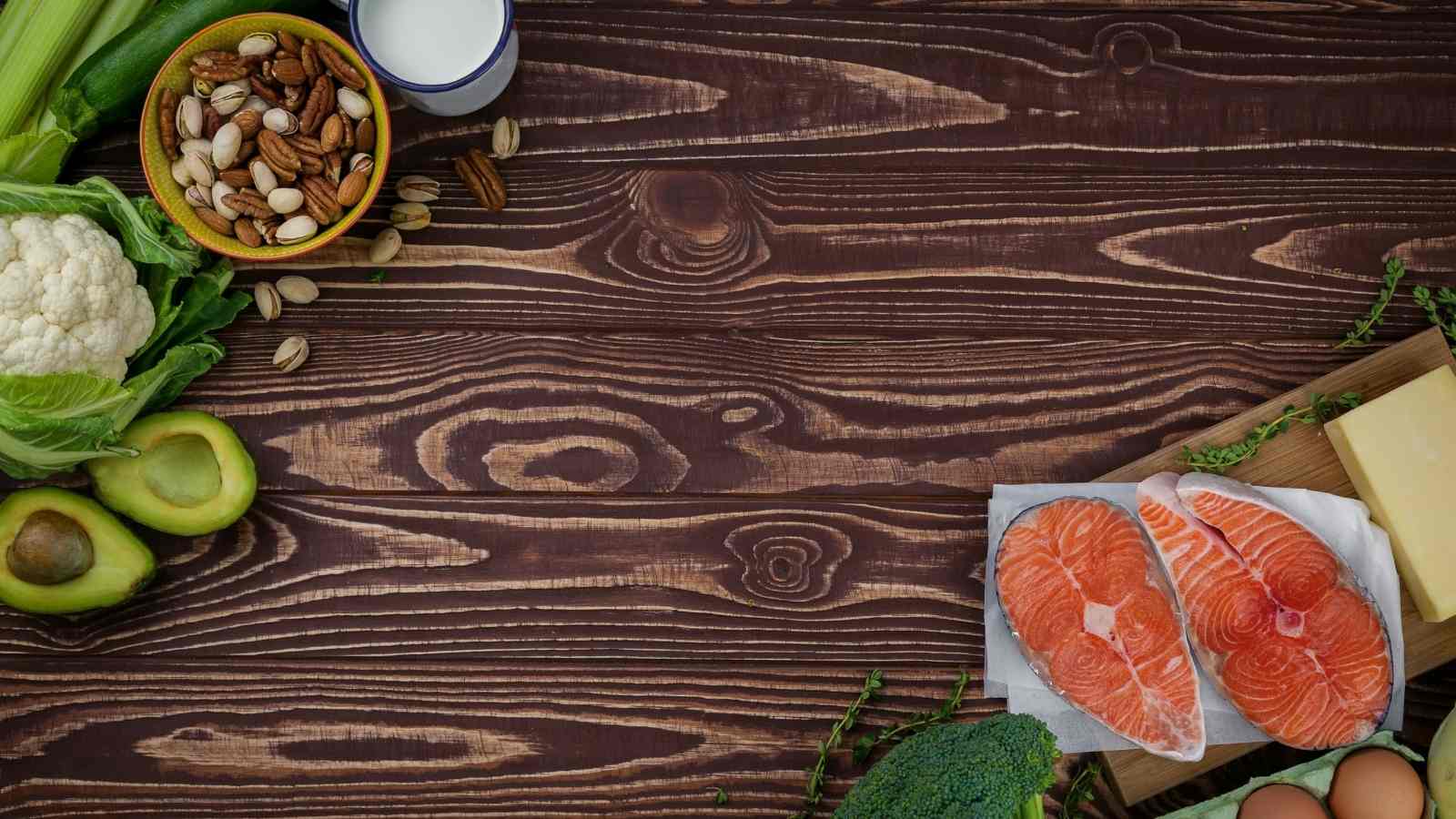

What Are Low-Carb Diets and How Do They Work?
Understanding the low carb versus keto diet requires a deeper understanding of each. The Low-Carb Diet is a wide category of dietary plans that restrict total carbohydrate consumption to less than 150 grammes per day. To guarantee that all ingested food is low in the Glycemic Index, limit your Net Carb consumption to 90-100g per day.
The term "low-carb diet" isn't well defined. Rather, it refers to a number of dietary plans that advocate for decreased carbohydrate consumption. The degree to which carb consumption is restricted varies across these dietary plans. All of them, however, suggest reducing carb consumption to a set amount and using a certain approach.
The majority of dietary advice is on reducing carb intake while boosting nutrient intake in some manner. Low-Carb Diets include LCHF (Low-Carb, High-Fat) Diets, Vegan Diets, Raw Food Diets (with some fruits), Vedic Diets, Mediterranean Diets, and others. The Ketogenic Diet, Paleo Diet, and Atkins Diet are all extreme low-carb diets. One of the most popular low-carb diets is the ketogenic diet. In the next portion of the essay, we'll learn more about the keto diet.
What Is A Keto Diet, Exactly?
A Ketogenic Diet, sometimes known as a "keto diet," is a low-carb diet. However, not all low-carb diets are Ketogenic Diets. Low-carb vs. keto is a pointless argument. Keto is, after all, a low-carb diet.
The ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate, moderate-protein, and high-fat diet. It's scientifically verified and happens as a result of an induced metabolic condition known as ketosis. Your body needs energy, which is mostly provided by carbohydrates. In normal circumstances, glycogen (essential sugar) is your energy source.
The Keto diet deprives your body of carbohydrates, causing it to enter Ketosis, a condition in which your body uses fats for energy when carbohydrates become scarce. This helps you lose weight quickly while also assisting you with chronic diseases such as Diabetes Type II, PCOD, and others. Adding those additional proteins to your diet may help you achieve healthier skin and hair.
The Keto Diet vs. the Low Carb Diet
You can't accomplish this with other standard diets because you're not just lowering carbohydrates, but you're also restricting them to the point where you're stimulating supportive ketone production.
Most significantly, the ketogenic diet is about more than just cutting carbs. It's all about the carbohydrate, protein, and fat ratios. On a keto diet, you should keep track of your protein and fat consumption as well as the quantity of carbohydrates you consume. Your net carb consumption is limited to 20-30 grammes per day on a normal keto diet.

The keto diet's main goal is to help you achieve and maintain healthy ketosis, which is a metabolic state in which the body consistently supplies and utilises ketones for fuel. To go into and stay in ketosis, all you have to do is keep your carb intake below 35 grammes per day.
Calculate your blood ketone levels to determine if you're on a keto diet or not. Have your ketone levels risen to 0.5 ml/L or higher after following the keto diet for a week or so? This indicates that you are on the keto diet, however, any reading below 0.5 ml/L indicates that you are on a low-carb diet, not a keto diet.
The following lines explain the difference between a low-carb and a ketogenic diet: There is no precise definition of what a "low-carb diet" is. Several studies define low-carb as an eating plan with carbohydrates that are less than 20% of total calories, while others classify it as a diet with carbs that are less than 45 percent of total calories. The key point on which many individuals tend to agree is the concept of the low-carb diet: lowering carb intake by eliminating carb-rich items.
More specifically, most low carb diets restrict foods high in effectively absorbable starches, such as sugar, bread, pasta, juice, and soft drinks, and replace them with foods high in fats and moderate protein, such as meat, poultry, fish, shellfish, eggs, cheddar, nuts, and seeds, as well as other low-starch foods, such as non-bland vegetables like spinach, kale, chard, and broccoli, as well as other vegetables and organic products, particularly beer. For best results, use keto products.
Summary
Low-carb diets are a kind of diet that has at least one feature that keeps your carb consumption to a bare minimum. The keto diet is one of the low-carb diets that is presently generating a lot of buzz.
Low-carb vs. keto is therefore not a point of contention. In truth, the ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate diet that aids in ketosis by restricting carbohydrate consumption, limiting protein intake, and enabling you to consume a large amount of healthy carbohydrates.




